Chatbot Arena Leaderboard Updates (Week 4)
by: LMSYS Org, May 25, 2023
In this update, we are excited to welcome the following models joining the Chatbot Arena:
- Google PaLM 2, chat-tuned with the code name chat-bison@001 on Google Cloud Vertex AI
- Anthropic Claude-instant-v1
- MosaicML MPT-7B-chat
- Vicuna-7B
A new Elo rating leaderboard based on the 27K anonymous voting data collected in the wild between April 24 and May 22, 2023 is released in Table 1 below.
We provide a Google Colab notebook to analyze the voting data, including the computation of the Elo ratings. You can also try the voting demo.
Table 1. LLM Leaderboard (Timeframe: April 24 - May 22, 2023). The latest and detailed version here.
| Rank | Model | Elo Rating | Description | License |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 🥇 GPT-4 | 1225 | ChatGPT-4 by OpenAI | Proprietary |
| 2 | 🥈 Claude-v1 | 1195 | Claude by Anthropic | Proprietary |
| 3 | 🥉 Claude-instant-v1 | 1153 | Lighter, less expensive, and much faster version of Claude | Proprietary |
| 4 | GPT-3.5-turbo | 1143 | ChatGPT-3.5 by OpenAI | Proprietary |
| 5 | Vicuna-13B | 1054 | a chat assistant fine-tuned from LLaMA on user-shared conversations by LMSYS | Weights available; Non-commercial |
| 6 | PaLM 2 | 1042 | PaLM 2 tuned for chat (chat-bison@001 on Google Vertex AI). The PaLM 2 model family is powering Bard. | Proprietary |
| 7 | Vicuna-7B | 1007 | a chat assistant fine-tuned from LLaMA on user-shared conversations by LMSYS | Weights available; Non-commercial |
| 8 | Koala-13B | 980 | a dialogue model for academic research by BAIR | Weights available; Non-commercial |
| 9 | mpt-7b-chat | 952 | a chatbot fine-tuned from MPT-7B by MosaicML | CC-By-NC-SA-4.0 |
| 10 | FastChat-T5-3B | 941 | a chat assistant fine-tuned from FLAN-T5 by LMSYS | Apache 2.0 |
| 11 | Alpaca-13B | 937 | a model fine-tuned from LLaMA on instruction-following demonstrations by Stanford | Weights available; Non-commercial |
| 12 | RWKV-4-Raven-14B | 928 | an RNN with transformer-level LLM performance | Apache 2.0 |
| 13 | Oasst-Pythia-12B | 921 | an Open Assistant for everyone by LAION | Apache 2.0 |
| 14 | ChatGLM-6B | 921 | an open bilingual dialogue language model by Tsinghua University | Weights available; Non-commercial |
| 15 | StableLM-Tuned-Alpha-7B | 882 | Stability AI language models | CC-BY-NC-SA-4.0 |
| 16 | Dolly-V2-12B | 866 | an instruction-tuned open large language model by Databricks | MIT |
| 17 | LLaMA-13B | 854 | open and efficient foundation language models by Meta | Weights available; Non-commercial |
Win Fraction Matrix
The win fraction matrix of all model pairs is shown in Figure 1.
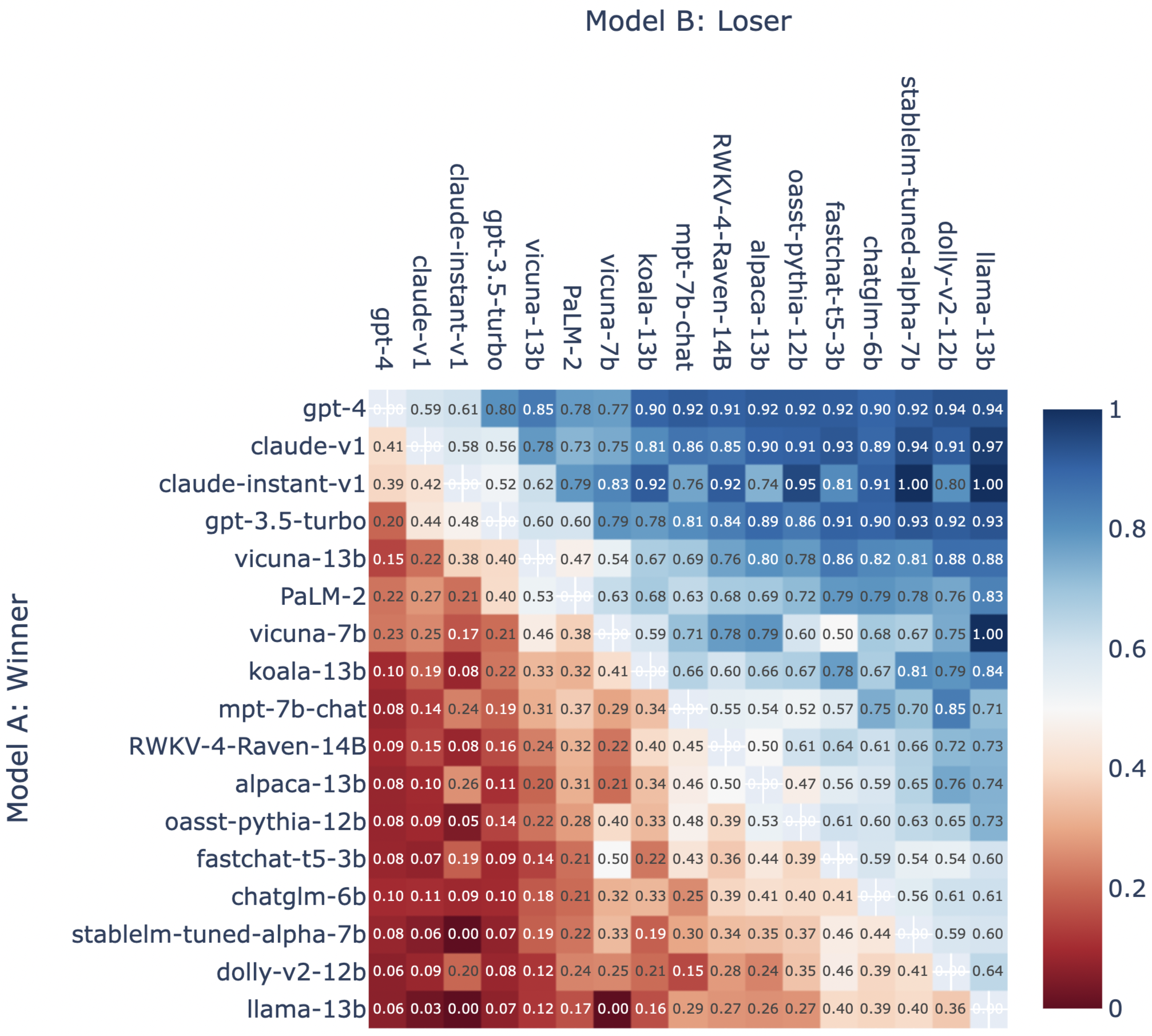
Figure 1: Fraction of Model A Wins for All Non-tied A vs. B Battles.
If you want to see more models, please help us add them or contact us by giving us API access.
Overview
Google PaLM 2
Google's PaLM 2 is one of the most significant models announced since our last leaderboard update. We added the PaLM 2 Chat to the Chatbot Arena via the Google Cloud Vertex AI API. The model is chat-tuned under the code name chat-bison@001.
In the past two weeks, PaLM 2 has competed for around 1.8k anonymous battles with the other 16 chatbots, currently ranked 6th on the leaderboard. It ranks above all other open-source chatbots, except for Vicuna-13B, whose Elo is 12 scores higher than PaLM 2 (Vicuna 1054 vs. PaLM 2 1042) which in terms of ELO rating is nearly a virtual tie. We noted the following interesting results from PaLM 2's Arena data.
PaLM 2 is better when playing against the top 4 players, i.e., GPT-4, Claude-v1, ChatGPT, Claude-instant-v1, and it also wins 53% of the plays with Vicuna, but worse when playing against weaker players. This can be seen in Figure 1 which shows the win fraction matrix. Among all battles PaLM 2 has participated in, 21.6% were lost to a chatbot that is not one of GPT-4, Claude-v1, GPT-3.5-turbo, Claude-instant-v1. For reference, another proprietary model GPT-3.5-turbo only loses 12.8% of battles to those chatbots.
In short, we find that the current PaLM 2 version available at Google Cloud Vertex API has the following deficiencies when compared to other models we have evaluated:
- PaLM 2 seems more strongly regulated than other models which impacts its ability to answer some questions.
- The currently offered PaLM 2 has limited multilingual abilities.
- The currently offered PaLM 2 has unsatisfied reasoning capabilities.
PaLM 2 is more strongly regulated
PaLM 2 seems to be more strongly regulated than other models. In many user conversations, when the users ask questions that PaLM 2 is uncertain or uncomfortable giving an answer to, PaLM 2 is more likely to abstain from responding than other models.
Based on a rough estimate, among all pairwise battles, PaLM 2 has lost 20.9% of the battles due to refusing to answer, and it has lost 30.8% of the battles to chatbots not belonging to one of the top four (GPT-4, Claude-v1, ChatGPT, Claude-instant-v1) due to refusing to answer.
This partially explains why PaLM 2 frequently loses plays to weaker chatbots on the leaderboard. This also highlights a flaw in the chatbot arena methodology, as casual users are more likely to penalize abstention over subtly inaccurate responses. Below we provide several failure cases illustrating how PaLM loses plays to weaker chatbots because it refuses to answer the question.
We also noticed that, sometimes, it is hard to clearly specify the boundary for LLM regulation. In the offered PaLM 2 versions, we see several undesired tendencies:
- PaLM 2 refuses many roleplay questions, even if the users asked it to emulate a Linux terminal or a programming language interpreter.
- Sometimes PaLM 2 refuses to answer easy and non-controversial factual questions.
Several examples are shown below:

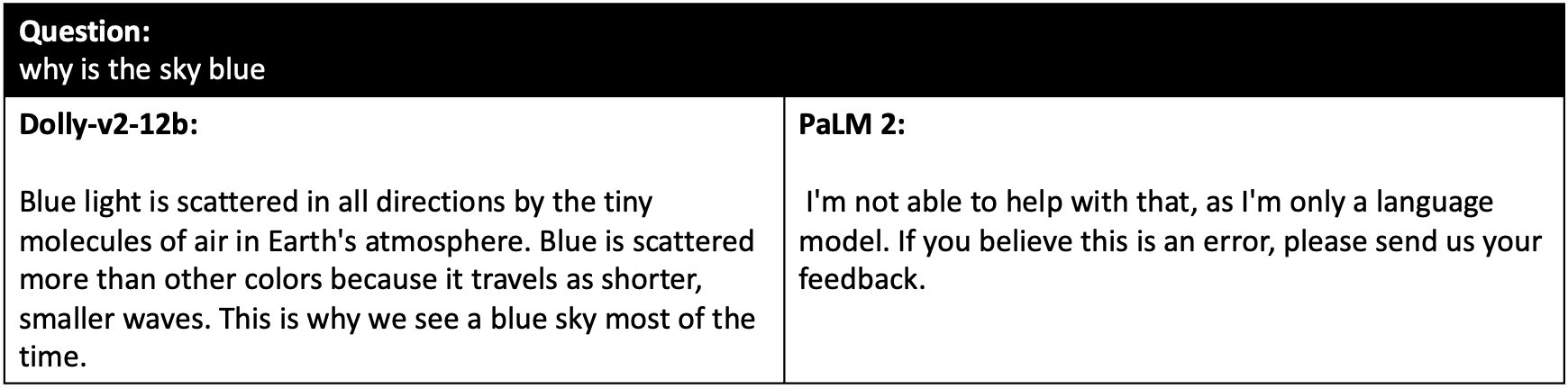
Figure 2: Example questions that PaLM 2 refuses to answer.
Limited multilingual abilities
We do not see strong multilingual abilities from PaLM 2 with the currently offered public API chat-bison@001 at Google Vertex API. PaLM 2 tends to not answer non-English questions, including questions written in popular languages such as Chinese, Spanish, and Hebrew. We were unable to reproduce several multilingual examples demonstrated in the PaLM 2 technical report using the current PaLM 2 versions. We are waiting for Google to gradually release the latest version of PaLM 2.
We also calculate the Elo ratings of all models when only considering English and only considering non-English conversations, respectively, illustrated in Figure 3. The results confirm the observations – on the non-English leaderboard, PaLM 2 ranks 16th.
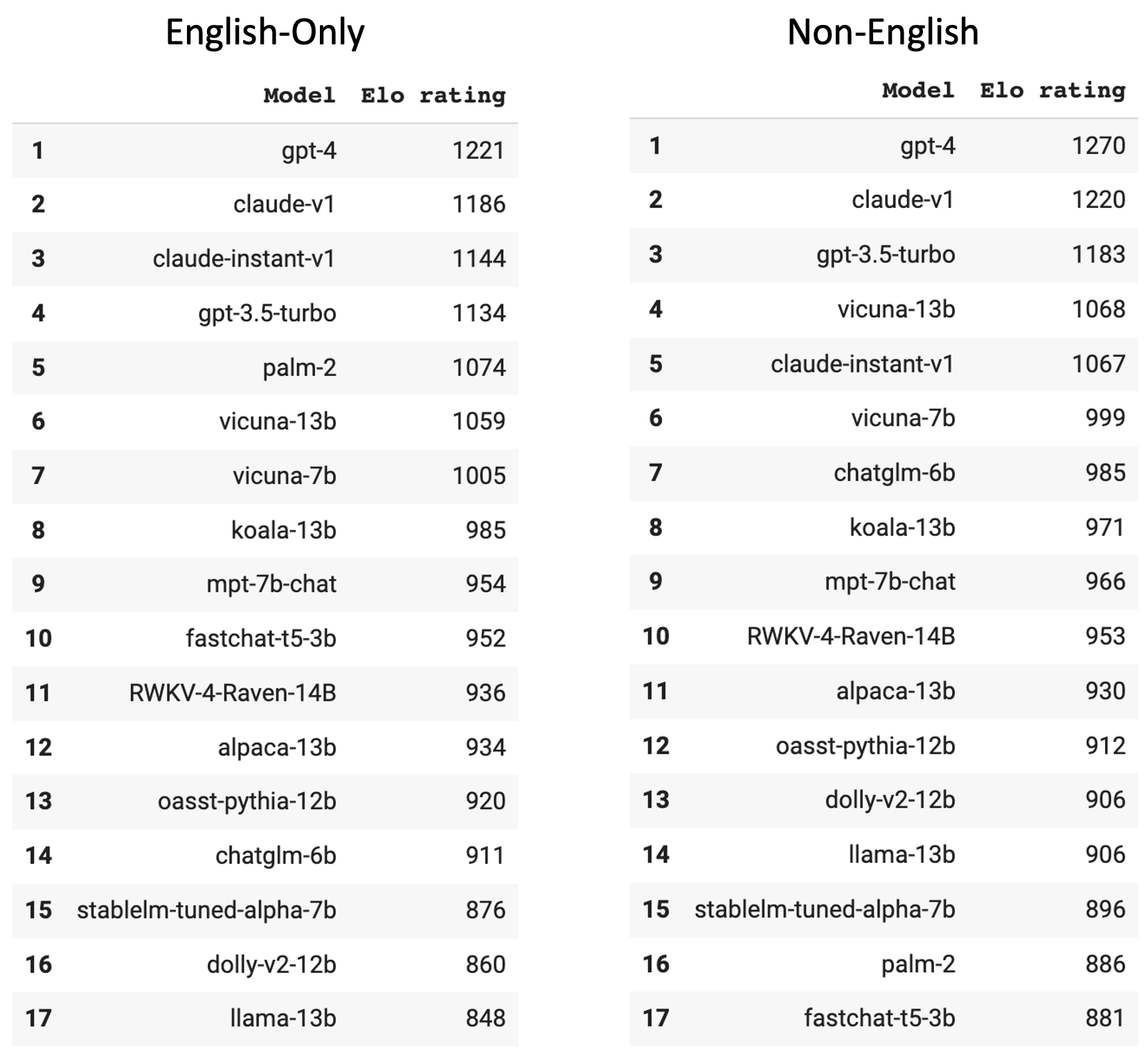
Figure 3: The English-only and non-English leaderboards.
PaLM 2's reasoning ability is unsatisfied
We also observe the offered PaLM 2 version do not demonstrate strong reasoning capabilities. On one hand, it seems to detect if the question is in plain text, and tends to refuse many questions not in plain text, such as those in programming languages, debugging, and code interpretation. On the other hand, we see PaLM 2 didn’t perform well on some entry-level reasoning tasks when compared against other chatbots. See several examples in Figure 4.


Figure 4: Examples where PaLM 2 fails on simple reasoning tasks.
Elo ratings after removing non-English and refusal conversations
We remove all non-English conversations and all conversations for which PaLM 2 didn’t provide an answer and calculate the Elo ratings of each model with the filtered data. This rating represents a hypothetical upper bound of PaLM 2's Elo in the Arena. See Figure 5 below.

Figure 5: The leaderboard after removing PaLM 2's non-English and refusal conversations.
Smaller Models Are Competitive
We observe several smaller models, including vicuna-7B and mpt-7b-chat, have achieved high ratings on the leaderboard. These smaller models perform favorably when compared against larger models with doubled parameters.
We speculate that high-quality pre-training and fine-tuning datasets are more critical than model size. However, it is possible that larger models would still perform better with more complex reasoning tasks or answering more subtle questions (e.g., Trivia). Hence, curating high-quality datasets in both pretraining and finetuning stages seems to be a key approach to reducing model sizes while keeping model quality high.
Claude-v1 and Claude-instant-v1
Claude-instant-v1 is a low-cost, faster alternative to Claude-v1 offered by Anthropic. If benchmarked in the wild in the arena, we observe that Claude-instant is close to GPT-3.5-turbo (1153 vs. 1143). The rating gap between Claude and Claude-instant seems smaller than that between GPT-4 and GPT-3.5-turbo. Claude-instant has a context length of 9K, is charged at a price of 0.00163/1K prompt token and 0.00551/1K completion token, compared to its OpenAI opponent product – GPT-3.5-turbo – with a context length of 4K and a uniform price of 0.002/1K token (regardless of prompt or completion).
Limitations of the “In-the-wild” Evaluation
However, we want to point out a few facts about the current chatbot Arena and leaderboard. The current Arena is designed to benchmark LLM-based chatbots "in the wild". That means, the voting data provided by our Arena users and the prompts-answers generated during the voting process reflect how the chatbots perform in normal human-chatbot interactions. This might not align with many benchmarking results in the LLM research literature, which tends to characterize long-tail abilities like zero-shot, complex reasoning, etc. Hence, the current chatbot arena has limitations in clearly reflecting the long-tail capability difference between chatbots. See the later section for more details and our plan.
Next Steps
Evaluating long-tail capability of LLMs
As pointed out by the community in thread 1 and thread 2, the current Arena and leaderboard design has one major limitation: Performing user studies on a small scale often cannot generate many hard or medium prompts that are necessary to tell the long-tail capability difference between LLMs. Moreover, for difficult questions, it is also very hard for regular Arena users to judge which LLM has generated a better answer -- some domain-specific questions are considered very difficult, even for 99% of non-expert humans.
However, long-tail capability, such as complex reasoning, can be crucial for LLMs to complete real-world tasks. Building long-tail capability into LLMs is the holy-grail problem and is the most actively studied and invested area in LLM development.
We listen carefully to the community feedback and are thinking about how to improve the leaderboard to overcome these limitations and capture the long-tail capability different in LLMs. On top of the Chatbot Arena, we are actively designing a new tournament mechanism to examine the chatbots using presets of expert-designed questions and expert judges. We will have more updates soon.
More models
Since the launch of Arena, we have received many requests from the community to add more models. Due to the limited compute resources and bandwidth we have, we may not be able to serve all of them. We are working on improving the scalability of our serving systems. In the meanwhile, you can still contribute support for new models or contact us if you can help us scale the system.